Quantitative PCR
Don Liu, Cecilia Schmidt, Tim Billings, and Muriel T. Davisson
Genotyping Ts65Dn mice is based on doing simultaneous quantitative PCR amplification of a gene or genes in the Ts65Dn chromosome and a control gene on another chromosome (in this case Apob) and comparing the average change (delta) in threshold cycle (CT) between the Ts65Dn genes and the control gene. Doing a multiplexed reaction with an internal control avoids the need for determining DNA concentration and permits a relatively large range of variation in concentration of template DNA.
Although trisomic females vary in transmission of the trisomy, the overall incidence of trisomy among progeny is only 19-25%. To streamline the typing process further the animals may be visually phenotyped before they are genotyped. The phenotype is variable and subtle, but to the trained eye the trisomic mice can be identified. Ts65Dn mice are usually smaller than their control littermates at weaning. When one lifts the cage cover slowly, the trisomic mice often raise their heads and bring their ears to the side. When picked up by the tail some trisomic mice make a high-pitched continuous squeak. Ts65Dn mice often display stereotypic behavior, repeatedly jumping up and down by the side of the cage. When a pencil is placed vertically in front of the mouse, controls will run around it, but Ts65Dn mice sit back on their haunches and "chatter." Phenotyping the mice is not 100% accurate, nor should it be relied upon to classify mice, but it does help eliminate control animals that are not needed and reduce the number of mice that must be genotyped. The combination of visual phenotyping followed by qPCR genotyping should make identifying Ts65Dn mice easier than chromosomal typing for most researchers.
Preparation of genomic DNA from mouse tail tips for PCR (28 samples; 26 test samples plus 2 controls, 1 Ts65Dn + 1 diploid)
- Labeled 1.5 ml Eppendorf tubes
- Place ~ 2 mm tail tip into each of the labeled tubes; try to use same size tail tip for all mice
- Aliquot 300 ul of 50 mM NaOH to each labeled tube
- Heat at 98° for 30 mins
- Vortex
- Return to heat for 30 mins or until sufficiently lysed
- Neutralize with 30 ul of 1 M Tris (pH8)
- Vortex
- Centrifuge for 6 mins at 14,000 RPM (IEC Micromax)
- Transfer supernatant to new tube. (Probably not necessary if you don't want to store the samples)
1M Tris
- 60.6g Tris Base [Sigma T1503-5kg]
- 500ml ddI H20
- Autoclave
50mM sodium hydroxide
- 2g sodium hydroxide [Fisher S318-500]
- 1 Liter ddI H20
- Autoclave
Standard curve
Note: Use large orifice tips throughout for DNA (see supplies list)
Use first DNA sample for standard curve determined from the four dilutions below.
Label four 1.5 ml Eppendorf tubes.
- Tube 1 1:50 10ul DNA / 490ul 10mM Tris
- Tube 2 1:100 200ul of 1:50 / 200ul 10mM Tris
- Tube 3 1:200 200ul of 1:100 / 200ul 10mM Tris
- Tube 4 1:400 200ul of 1:200 / 200ul 10mM Tris
Label 27 Eppendorf 1.5 ml tubes (samples 2-28)
- 1:100 dilution: 10ul DNA + 990ul 10mM Tris
10mM Tris
- 1ml 1M Tris [1M Tris HCL pH8 (Invitrogen # 15568-025) 1000ml]
- 100ml d H20 [Gibco d H20 # 15230-170]
Prepare master mix (on ice)
Prepare enough mix for 3 reactions of each DNA sample, a standard curve, two control samples, plus 3 reactions for no template control (NTC). For a whole 96-well plate, 102 reactions in total are needed ( allow 6 extra reactions for pipetting errors). The reaction mix contains a probe and forward and reverse primers for either the amyloid beta precursor protein gene (App) or the myxovirus resistance 1 gene (Mx1) and the apolipoprotein B control gene (Apob).
Here is an example of using App and Apob for a multiplex reaction:
|
|
1RXN |
102 RXN's |
|---|---|---|
|
2X Master Mix |
12.5ul |
1275ul |
|
IMR 1863 40UM |
0.25ul |
25.5ul |
|
IMR 1864 40uM |
0.25ul |
25.5ul |
|
IMR 1544 40uM |
0.25ul |
25.5ul |
|
IMR 1545 40uM |
0.25ul |
25.5ul |
|
TMoIMR023 5uM |
0.75ul |
76.5ul |
|
TMoIMR032 5uM |
0.75ul |
76.5ul |
|
H2O |
0 |
|
|
Total |
15ul |
1530ul |
|
DNA (1:200 dilution) |
10ul |
|
|
|
25ul |
|
Load 96-well optical plate (see below) adding DNA last
- 15 ul reaction mix per well
- 10 ul DNA (1:100 dilution)
Layout of the optical plate as we load it is shown below. The blank squares below are the two additional repeats for each sample.
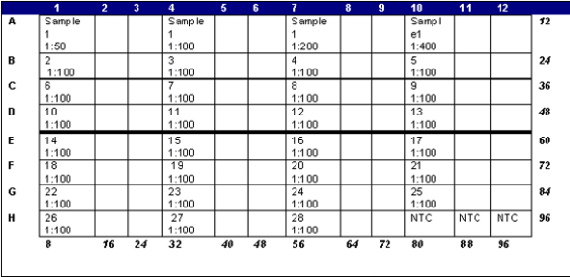
Place the optical adhesive cover over the plate, taking care not to touch the cover. Smooth with seal applicator and cover with compression pad. Centrifuge briefly (IEC HN-S 11 centrifuge) before putting on machine.
|
Cycles |
|
|---|---|
|
50°C |
2 mins |
|
95°C |
10 mins |
|
95°C |
15 secs* |
|
60°C |
1 min* |
|
*40 cycles |
|
Probes
TMoIMR023 Vic - CCA ATG GTC GGG CAC TGC TCA A - Tamra
Apob control, This probe is used with primers IMR1544 and IMR 1545.
TMoIMR032 6FAM-CAA AGG CGC CAT CAT CGG ACT CA- Tamra
App probe for Ts65Dn mice. This probe is used with primers IMR1863 and IMR1864. Probe designed by Don Liu.
TmoIMR041 6FAM-Tgg CTT TCC TGG TCG CTG TGC A-Tamra.
Mx1 probe for Ts65Dn mice. This probe is used with primers IMR2077 and IMR2078. Probe designed by Don Liu.
Primers
IMR 1544 5' - CAC GTG GGC TCC AGC ATT -3' Apob forward
Taqman control forward primer.
GenBank Accession #U82624.
IMR 1545 5' - TCA CCA GTC ATT TCT GCC TTT G - 3' Apob reverse
Taqman control forward primer.
GenBank Accession #U82624.
IMR 1863 5'-TGC TGA AGA TGT GGG TTC GA-3'
These App primers were created for Taqman analysis of Ts65Dn mice. Sequence based on App gene exon 17 nt4895 to 5041.
GenBank Accession #U82624, nt 4903-4922
Primer designed by Don Liu.
IMR 1864 5'-GAC AAT CAC GGT TGC TAT GAC AA-3'
Sequence based on App gene exon 17 nt4895 to 5041.
GenBank Accession #U82624 nt 4981-4959
Primer designed by Don Liu.
IMR 2077 5'-TCT CCG ATT AAC CAG GCT AGC TAT-3'
These Mx1 primers were created for Taqman analysis of a second gene to confirm the App Taqman assay on Ts65Dn mice. Sequence based on Mx1 gene exon14.
GenBank Accession #M21117, nt316-339
Primer designed by Don Liu.
IMR 2078 5'-GAC ATA AGG TTA GCA GCT AAA GGA TCA-3'
Sequence based on Mx1 gene exon14.
GenBank Accession #M21117. nt 341-362
Primer designed by Don Liu.
Reference
Liu DP, Schmidt C, Billings T, Davisson MT. 2003. Quantitative PCR genotyping assay for the Ts65Dn mouse model of Down syndrome. BioTechniques 35(6):1170-4, 1176, 1178 passim.